Boolean Logic II
(Usage hints for this presentation)
IT Systems, Summer Term 2026
Dr.-Ing. Matthes Elstermann
1. Introduction
- Part 1
- Break for self-study
- Part 2
2. Boolean Circuits
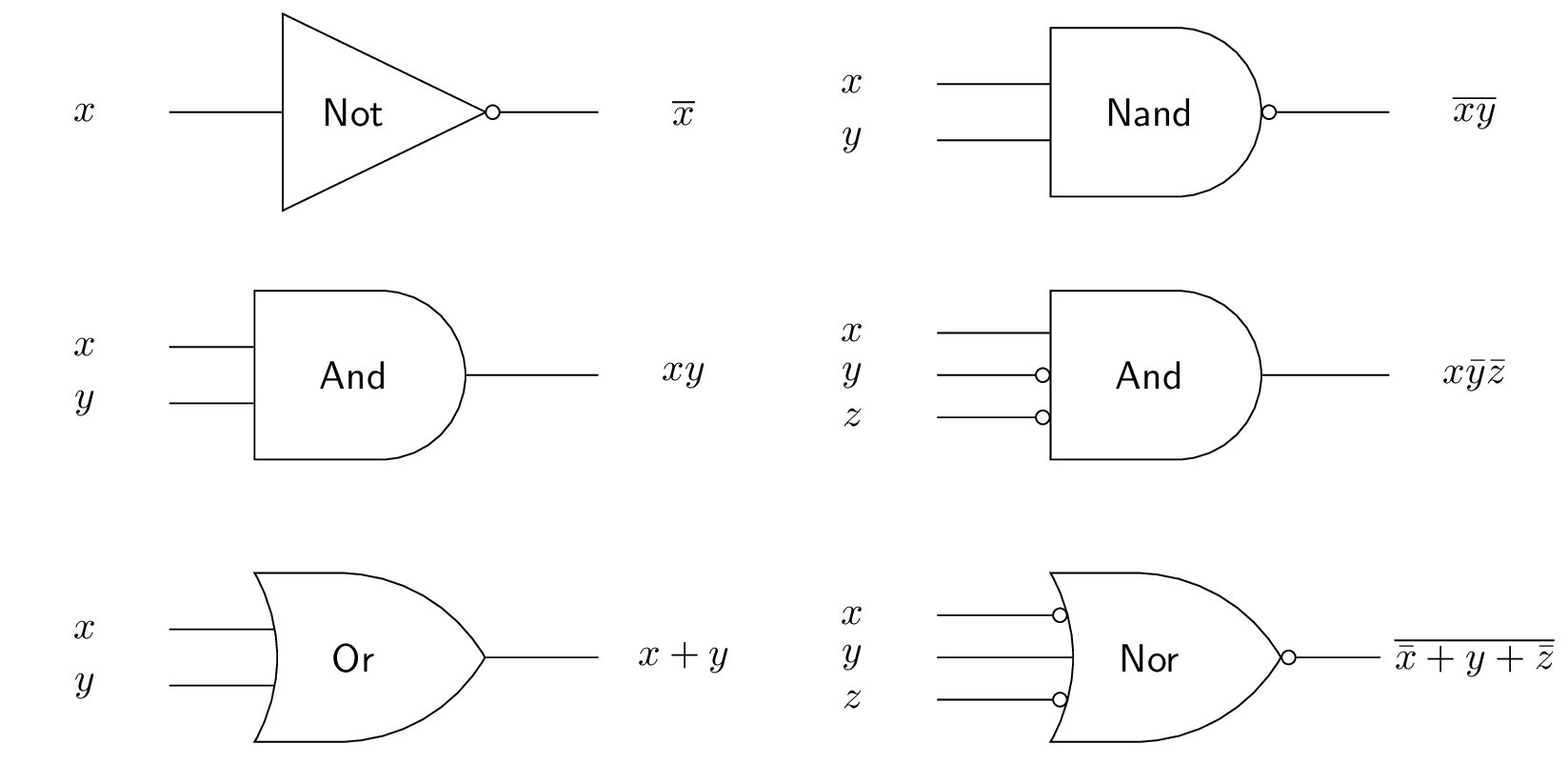
2.1. Symbols for Logical Gates
2.2. Fan-In and Circuits
Gate’s interface defines number of inputs
- Gates and chips have pins for inputs and outputs
Number of inputs called fan-in
Fan-in is 2 for
Nand,And,Orin case of Nand2TetrisWith associative and commutative operations, gates of any fan-in work in any order of computation
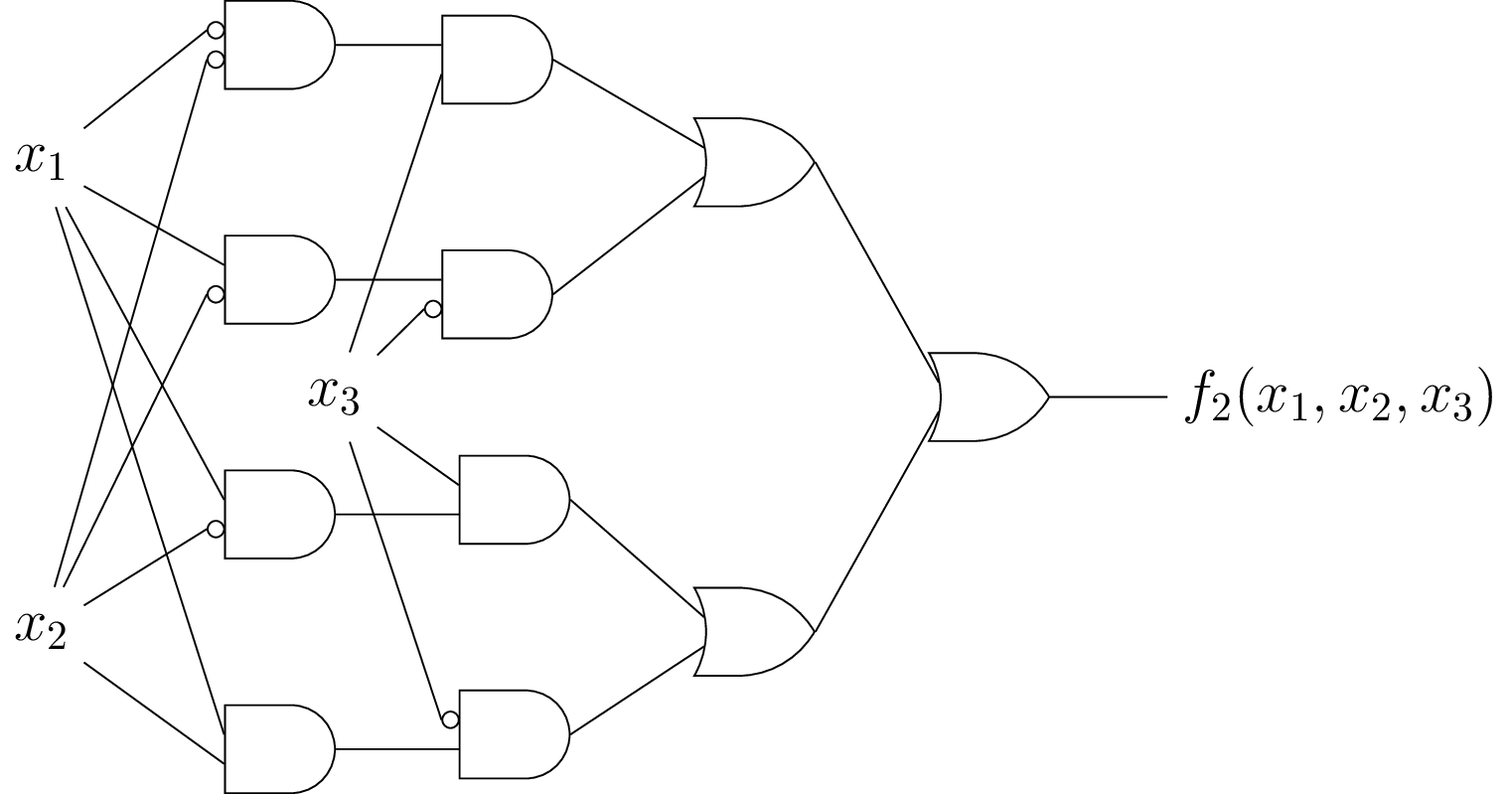
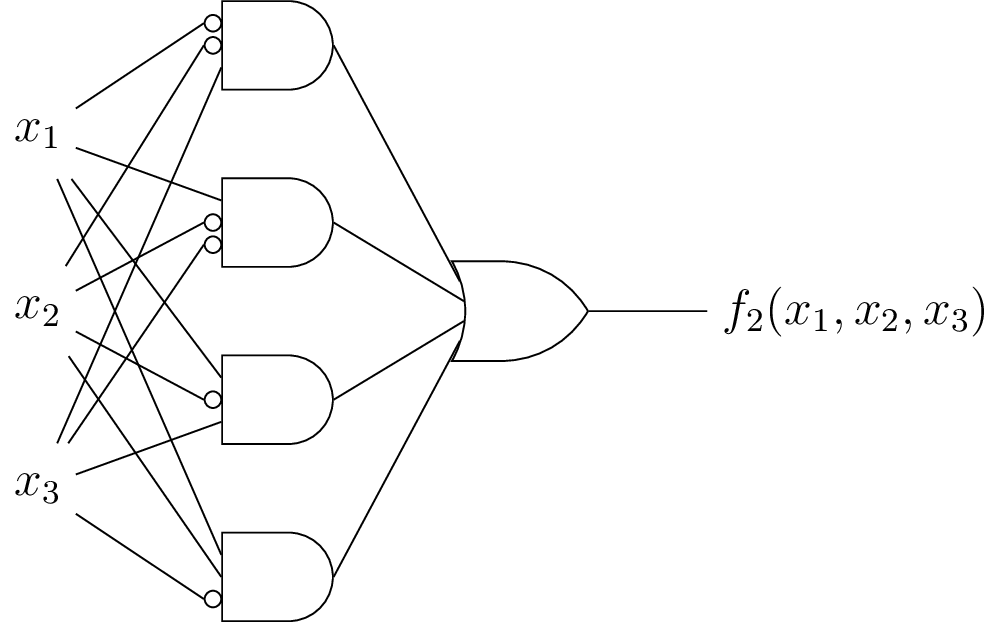
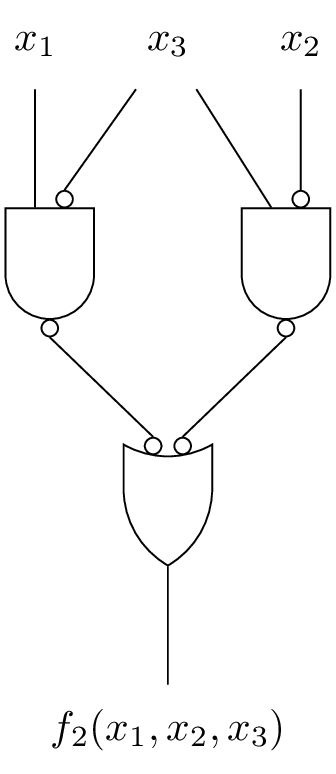
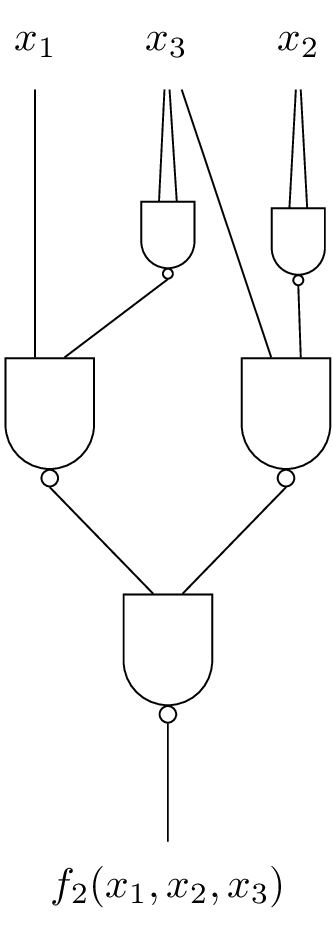
Consider
\begin{eqnarray*} &&f_2(x_1, x_2, x_3) = \\ && \bar{x_1}\bar{x_2}x_3 + x_1\bar{x_2}\bar{x_3} + x_1\bar{x_2}x_3 + x_1 x_2 \bar{x_3} \end{eqnarray*}\(x_1\) \(x_2\) \(x_3\) \(f_2(x_1, x_2, x_3)\) 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 1 0 0 0 1 1 0 1 0 0 1 1 0 1 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 1 0
2.3. Multi-Bit and Multi-Way Gates
- Multi-bit gates/chips: Inputs are n-bit operands each
- E.g.,
And16: And for 16-bit numbers is applied bit-by-bitAnd16(1100110011001100, 00001111000011110000) = 0000110000001100- Use 16
Andgates in implementation
- E.g.,
- Multi-way gates/chips: More than 2 inputs, i.e., fan-in larger than 2
- E.g.,
Or8Way: 8 inputs;out = 1if at least one of them is 1- Use suitable number of
Orgates in implementation
- Use suitable number of
- E.g.,
3. Sample Transformations
3.1. Sample Algebraic Simplifications
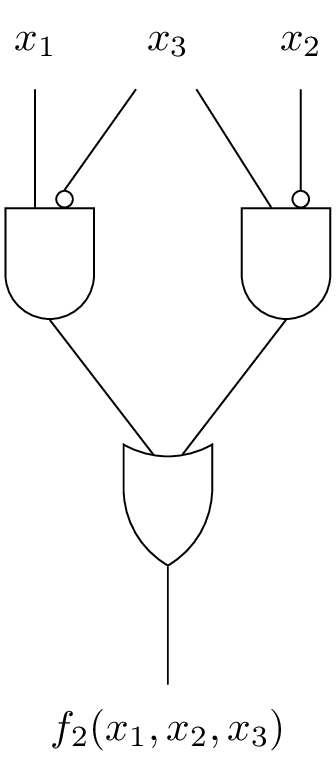
Simplify \(f_2(x_1, x_2, x_3)\)
\begin{eqnarray*} &&= \color{darkred}{\bar{x_1}\bar{x_2}x_3} + \color{darkblue}{x_1\bar{x_2}\bar{x_3}} + \color{darkred}{x_1\bar{x_2}x_3} + \color{darkblue}{x_1 x_2 \bar{x_3}}\\ &&= \color{darkred}{(\bar{x_1} + x_1)\bar{x_2}x_3} + \color{darkblue}{(\bar{x_2} + x_2)x_1\bar{x_3}}\\ &&= \color{darkred}{\bar{x_2}x_3} + \color{darkblue}{x_1\bar{x_3}} \end{eqnarray*}
Simplify \(\bar{x_1}\bar{x_2}x_3 + x_1\bar{x_2}x_3 + x_1 x_2 x_3\)
- \(\color{darkred}{\bar{x_1}\bar{x_2}x_3} + \color{darkred}{x_1\bar{x_2}x_3} + \color{darkblue}{x_1\bar{x_2}x_3} + \color{darkblue}{x_1 x_2 x_3}\)
\(\color{darkred}{(\bar{x_1} + x_1)\bar{x_2}x_3} + \color{darkblue}{(\bar{x_2} + x_2)x_1x_3}\)
3.2. DNF to All-Nand, Graphically
4. Multiplexors and De-Multiplexors, Project 1
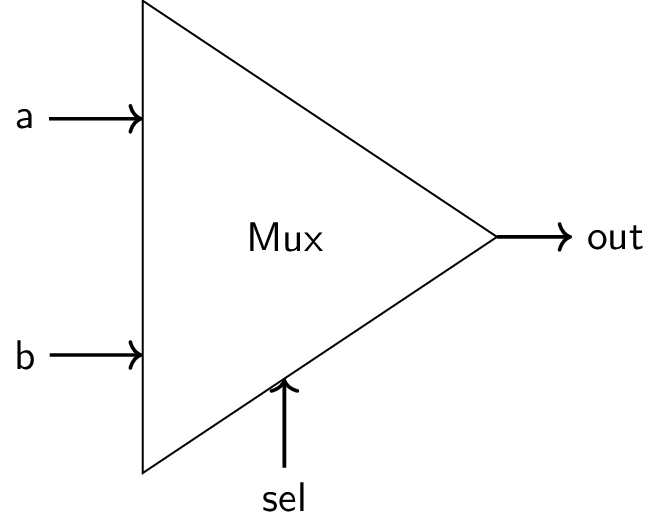
4.1. Mux
Truth table
a b sel out 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 0 0 1 1 0 1 0 1 1 0 1 1 1 1 1
Specification (from
Mux.hdl)If sel==1 then out=b else out=a.
Alternative view on truth table
sel out 0 a 1 b
- Self-study
- Implement
Mux- Start from truth table, simplify (task in Learnweb)
- Use Not, And, Or gates
- Implement
- Maybe in class
- Implement
Mux8Way16
- Implement
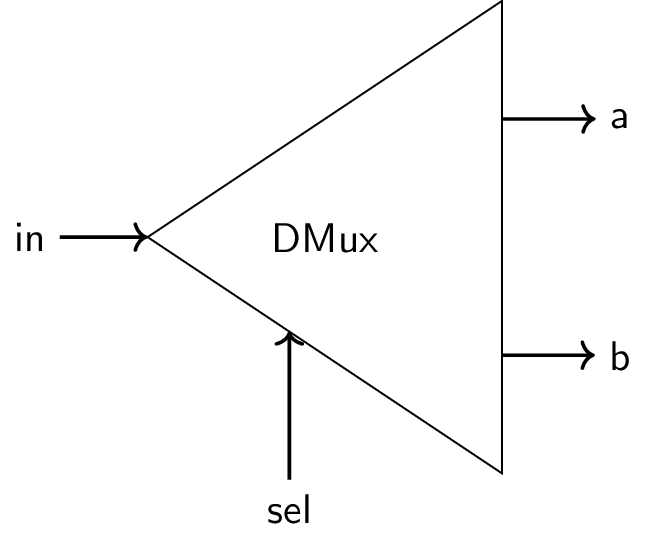
4.2. DMux
Truth table
in sel a b 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 1 0 1 1 0 1
- Self-study
- Implement
DMux- Read from truth table
- Use one Not, two And gates
- Implement
- Maybe in class
- Implement
DMux8Way
- Implement
4.3. Project 1
Given:
Nand(a,b),falsea b Nand(a, b) 0 0 1 0 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 0 - Build:
- Not(a) = …
- true = …
- And(a,b) = …
- Or(a,b) = …
- Mux(a,b,sel) = …
- Etc. - 12 gates altogether
- See Chapter 1 of (Nisan and Schocken 2005)
5. Conclusions
5.1. Summary
- Boolean logic is formal foundation for functionalities of gates and chips
- DNF provides canonical representation for Boolean functions
- Can be read off truth table
- Simplification with laws
- Project 1 builds on Boolean logic to construct gates and circuits
- Starting from {Nand}, which is functionally complete
5.2. Q&A
- Please ask questions and provide feedback on a regular basis
Bibliography
License Information
Source files are available on GitLab (check out embedded submodules) under free licenses. Icons of custom controls are by @fontawesome, released under CC BY 4.0.
Except where otherwise noted, the work “Boolean Logic II”, © 2024-2025 Jens Lechtenbörger, is published under the Creative Commons license CC BY-SA 4.0.